貨號(hào)
產(chǎn)品規(guī)格
售價(jià)
備注
BN40306R-100ul
100ul
¥2360.00
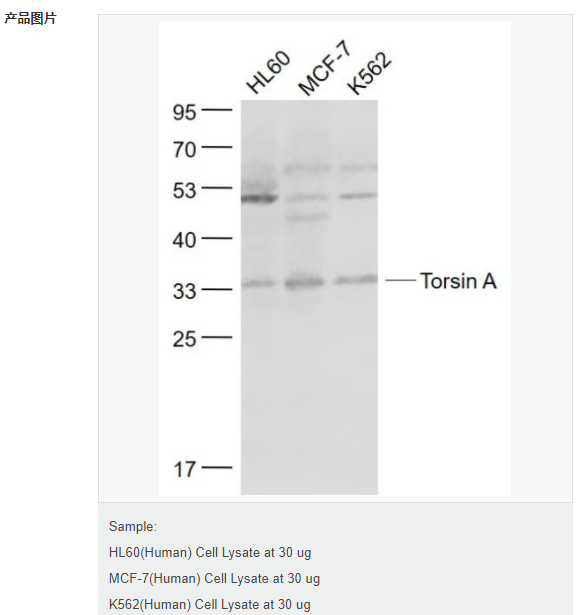
交叉反應(yīng):Human(predicted:Mouse,Rat,Dog,Pig,Cow) 推薦應(yīng)用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,ELISA
BN40306R-200ul
200ul
¥3490.00
交叉反應(yīng):Human(predicted:Mouse,Rat,Dog,Pig,Cow) 推薦應(yīng)用:WB,IHC-P,IHC-F,ICC,IF,ELISA
產(chǎn)品描述
| 英文名稱 | Torsin A |
| 中文名稱 | 扭轉(zhuǎn)蛋白A抗體 |
| 別 名 | DQ2; Dystonia 1; Dystonia 1 protein; Dyt1; Tor1a; Torsin A; Torsin family 1 member A; TOR1A_HUMAN. |
| 研究領(lǐng)域 | 細(xì)胞生物 神經(jīng)生物學(xué) |
| 抗體來源 | Rabbit |
| 克隆類型 | Polyclonal |
| 交叉反應(yīng) | Human, (predicted: Mouse, Rat, Dog, Pig, Cow, ) |
| 產(chǎn)品應(yīng)用 | WB=1:500-2000 ELISA=1:5000-10000 IHC-P=1:100-500 IHC-F=1:100-500 ICC=1:100-500 IF=1:100-500 (石蠟切片需做抗原修復(fù)) not yet tested in other applications. optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
| 分 子 量 | 35kDa |
| 細(xì)胞定位 | 細(xì)胞核 細(xì)胞漿 細(xì)胞膜 |
| 性 狀 | Liquid |
| 濃 度 | 1mg/ml |
| 免 疫 原 | KLH conjugated synthetic peptide derived from human Torsin A:56-130/332 |
| 亞 型 | IgG |
| 純化方法 | affinity purified by Protein A |
| 儲(chǔ) 存 液 | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| 保存條件 | Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| PubMed | PubMed |
| 產(chǎn)品介紹 | A mutation of the DYT1 gene, which codes for TorsinA, has been identified as the cause of one form of autosomal dominantly inherited dystonia. Early-onset torsion dystonia is a movement disorder, characterized by twisting muscle contractures, that begins in childhood. Symptoms are believed to result from altered neuronal communication in the basal ganglia. TorsinA comprises 332 amino acids. TorsinA is widely expressed throughout the mouse central nervous system and is detected in the majority of neurons in nearly all regions. The proteins display cytoplasmic distribution, although in some types of neurons localization is perinuclear. TorsinA often performs chaperone-like functions that assist in the assembly, operation, or dis-assembly of protein complexes. The gene which encodes TorsinA has high homology to three additional mammalian genes and a nematode gene and distal similarity to the family of heat-shock proteins and the Clp protease family. The gene which encodes TorsinA maps to human chromosome 9q34. Function: May serve as a molecular chaperone assisting in the proper folding of secreted and/or membrane proteins. In the nucleus, displaces the nuclear membrane proteins SUN2, SYNE2 and nesprin-3/C14orf49, leaving nuclear pores and SUN1 unchanged. Subunit: May form homohexamers. Interacts with TOR1AIP1 and TOR1AIP2. Interacts with KLHL14, preferentially when ATP-free. Subcellular Location: Endoplasmic reticulum lumen. Nucleus membrane. Note=Mainly located in the lumen of the endoplasmic reticulum. The association with nuclear envelope is mediated by the interaction with TOR1AIP2. The Glu-303 del variant is lumenally-oriented in discrete large spheroid intracellular structures rather than in the endoplasmic reticulum. Tissue Specificity: Widely expressed. Highest levels in kidney and liver. Not detected in spleen. In the brain, high levels found in the dopaminergic neurons of the substantia nigra pars compacta, as well as in the neocortex, hippocampus and cerebellum. Also high expression in the spinal cord. DISEASE: Defects in TOR1A are the cause of dystonia type 1 (DYT1) [MIM:128100]. DYT1 is a primary torsion dystonia, and the most common and severe form. Dystonia is defined by the presence of sustained involuntary muscle contractions, often leading to abnormal postures. DYT1 is characterized by involuntary, repetitive, sustained muscle contractions or postures involving one or more sites of the body, in the absence of other neurological symptoms. Typically, symptoms develop first in an arm or leg in middle to late childhood and progress in approximately 30% of patients to other body regions (generalized dystonia) within about five years. 'Torsion' refers to the twisting nature of body movements observed in DYT1, often affecting the trunk. Distribution and severity of symptoms vary widely between affected individuals, ranging from mild focal dystonia to severe generalized dystonia, even within families. Similarity: Belongs to the clpA/clpB family. Torsin subfamily. SWISS: O14656 Gene ID: 1861 Database links: Entrez Gene: 1861 Human Entrez Gene: 30931 Mouse Omim: 605204 Human SwissProt: O14656 Human SwissProt: Q9ER39 Mouse Unigene: 534312 Human Unigene: 154994 Mouse Important Note: This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |