貨號
產(chǎn)品規(guī)格
售價
備注
BN42108R-50ul
50ul
¥2020.00
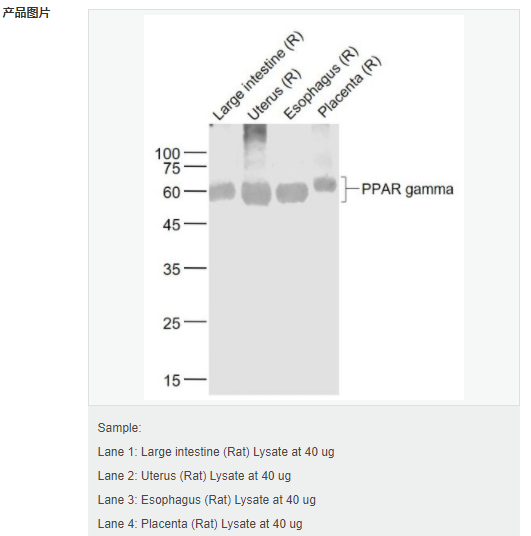
交叉反應(yīng):Rat(predicted:Human,Mouse) 推薦應(yīng)用:WB
BN42108R-100ul
100ul
¥3240.00
交叉反應(yīng):Rat(predicted:Human,Mouse) 推薦應(yīng)用:WB
產(chǎn)品描述
| 英文名稱 | PPAR gamma |
| 中文名稱 | 過氧化酶活化增生受體γ重組兔單克隆抗體 |
| 別 名 | CIMT1; HUMPPARG; NR1C3; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group C member 3; PAX8/PPARG Fusion Gene; Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor gamma; PPAR gamma; PPARG; PPARG1; PPARG2; PPARG3; CIMT1; GLM1; HUMPPARG; NR1C3; Nuclear receptor subfamily 1 group C member 3; PAX8/PPARG Fusion Gene; Peroxisome proliferator activated nuclear receptor gamma variant 1; Peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma 1; Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor gamma; Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma; PPAR gamma; PPAR-gamma; PPARG_HUMAN; PPAR gamma 1; PPAR gamma 2; PPAR gamma 3; PPAR gamma-1; PPAR gamma-2; PPAR gamma-3. |
| 研究領(lǐng)域 | 免疫學(xué) 信號轉(zhuǎn)導(dǎo) 轉(zhuǎn)錄調(diào)節(jié)因子 激酶和磷酸酶 糖尿病 內(nèi)分泌病 |
| 抗體來源 | Rabbit |
| 克隆類型 | Monoclonal |
| 克 隆 號 | 45G1 |
| 交叉反應(yīng) | Rat, (predicted: Human, Mouse, ) |
| 產(chǎn)品應(yīng)用 | WB=1:1000-2000 not yet tested in other applications. optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the end user. |
| 分 子 量 | 57kDa |
| 細胞定位 | 細胞核 |
| 性 狀 | Liquid |
| 濃 度 | 1mg/ml |
| 免 疫 原 | Recombinant human PPAR gamma protein, around 100-200aa: |
| 亞 型 | IgG |
| 純化方法 | affinity purified by Protein A |
| 儲 存 液 | 0.01M TBS(pH7.4) with 1% BSA, 0.03% Proclin300 and 50% Glycerol. |
| 保存條件 | Shipped at 4℃. Store at -20 °C for one year. Avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles. |
| PubMed | PubMed |
| 產(chǎn)品介紹 | The PPAR gamma antibody mainly is exist in the white fat organization, the fat for the PPAR gamma is born, blood sugar stability, the disease respond, the artery gruel kind hardens to rise the important function with the tumor occurrence of etc. all, but concerning the PPAR gamma to bone of function is a new research heat to order in recent years.A PPAR of many researches report gamma was go together with the body is after activate can the function promote many capable cells divided to increase to living but repress the ossification cell to divide to cause the bone measure the decrease or bone softs toward the fat cell in the marrow, the PPAR gamma promotes the ability and bones that the fat cell divide metabolize closely related, the performance is increasing along with the growth marrow fat content of the age, the ossification cell metabolism the outcome reduce, the different construction PPAR gamma 2 have the important function. Function: Receptor that binds peroxisome proliferators such as hypolipidemic drugs and fatty acids. Once activated by a ligand, the receptor binds to a promoter element in the gene for acyl-CoA oxidase and activates its transcription. It therefore controls the peroxisomal beta-oxidation pathway of fatty acids. Key regulator of adipocyte differentiation and glucose homeostasis. Subunit: Forms a heterodimer with the retinoic acid receptor RXRA called adipocyte-specific transcription factor ARF6. Interacts with NCOA6 coactivator, leading to a strong increase in transcription of target genes. Interacts with coactivator PPARBP, leading to a mild increase in transcription of target genes. Interacts with FAM120B. Interacts with PRDM16. Interacts with NOCA7 in a ligand-inducible manner. Interacts with NCOA1 LXXLL motifs. Interacts with TGFB1I1. Interacts with DNTTIP2. Interacts with PRMT2. Subcellular Location: Nucleus. Tissue Specificity: Highest expression in adipose tissue. Lower in skeletal muscle, spleen, heart and liver. Also detectable in placenta, lung and ovary. DISEASE: Note=Defects in PPARG can lead to type 2 insulin-resistant diabetes and hyptertension. PPARG mutations may be associated with colon cancer. Defects in PPARG may be associated with susceptibility to obesity (OBESITY) [MIM:601665]. It is a condition characterized by an increase of body weight beyond the limitation of skeletal and physical requirements, as the result of excessive accumulation of body fat. Defects in PPARG are the cause of familial partial lipodystrophy type 3 (FPLD3) [MIM:604367]. Familial partial lipodystrophies (FPLD) are a heterogeneous group of genetic disorders characterized by marked loss of subcutaneous (sc) fat from the extremities. Affected individuals show an increased preponderance of insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus and dyslipidemia. Genetic variations in PPARG can be associated with susceptibility to glioma type 1 (GLM1) [MIM:137800]. Gliomas are central nervous system neoplasms derived from glial cells and comprise astrocytomas, glioblastoma multiforme, oligodendrogliomas, and ependymomas. Note=Polymorphic PPARG alleles have been found to be significantly over-represented among a cohort of American patients with sporadic glioblastoma multiforme suggesting a possible contribution to disease susceptibility. Similarity: Belongs to the nuclear hormone receptor family. NR1 subfamily. Contains 1 nuclear receptor DNA-binding domain. SWISS: P37231 Gene ID: 5468 Database links: Entrez Gene: 5468 Human Entrez Gene: 19016 Mouse SwissProt: P37231 Human SwissProt: P37238 Mouse Unigene: 162646 Human Unigene: 3020 Mouse Unigene: 23443 Rat Important Note: This product as supplied is intended for research use only, not for use in human, therapeutic or diagnostic applications. |